STUDY SKILLS
Good study skills can make it easier for you to learn a new language. They can also help you to achieve your personal best and persevere when it is necessary. Effective learning depends not on how much time you spend studying, but on how well you use your time. The study skills section will help you to study smarter, focus better and achieve more while preparing for IELTS.
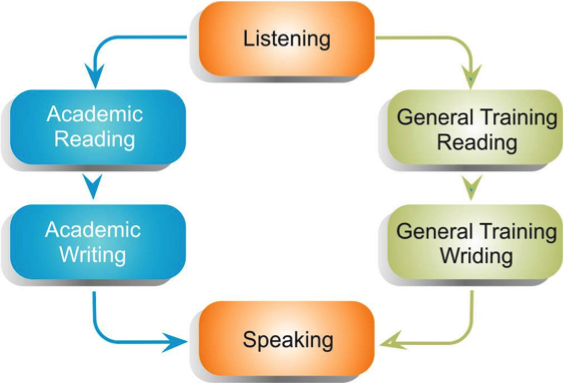
IELTS ACADEMIC OR IELTS GENERAL TRAINING?
IELTS is recognised by universities, colleges, professional organisations, government authorities and employers in many countries where English is the main language of communication.
There are two exam versions:
The IELTS ACADEMIC MODULE, which is for candidates who wish to study at undergraduate or postgraduate levels, or to register with a professional body and the
IELTS GENERAL TRAINING MODULE, which is for candidates who wish to migrate to and work in an English-speaking country.
IT’S A GOOD IDEA to contact the organisation you are applying to in order to check their entry requirements. Make sure you know which of the two versions you will need to do and what score on the IELTS nine-band scale is required. You can also seek advice from www.ielts.org.
The IELTS Listening
HOW TO THINK IN ENGLISH
If you want to express yourself clearly in English in the IELTS exam, you need to think in English and not try to translate your thoughts and words from your native language into English.
A simple and effective way to think in English is to construct a correct sentence in English. That is, you have to arrange the words in the correct order. The basic sentence patterns in English are the following:
- SUBJECT + VERB
Temperatures have risen. - SUBJECT + VERB (appear, be, become, etc) + COMPLEMENT
The process is complicated. - SUBJECT + VERB + OBJECT.
The scientist attended the conference. - SUBJECT + VERB + indirect OBJECT + direct OBJECT.
The students offered their teacher a present. - SUBJECT + VERB + direct OBJECT + COMPLEMENT
I think his work is remarkable.
The most common order of the different elements of a sentence in English is 1) WHO. 2) WHAT. 3) HOW. 4) WHERE. 5) WHEN and 6) WHY.
e.g The sale of cars decreased dramatically in Europe in 2008 because of an economic recession.
However, with verbs of movement or direction the order of the different elements of a sentence is 1)WHO. 2)WHAT. 3) WHERE. 4) HOW. 5) WHEN and 6) WHY.
e.g Many people travel to work by public transport every day because it is more convenient.
If you learn the basic word order in English, you will improve your listening comprehension since you will be able to predict what kind of information will follow. You will also improve your own fluency in writing and speaking because you will be able to stop thinking in your native language and avoid translating word for word into English.
JG.
IELTS EXAM PAST PAPERS:
HOW THEY CAN HELP YOU
The #IELTS Exam tests your knowledge, understanding and ability to communicate in the English language under timed conditions.
The key to success in any exam is to be prepared. It is important to know the type of questions that are set and to learn the knowledge and skills needed to succeed. Past papers can help you to prepare and revise effectively for the exam.
Use past #IELTS exam papers to learn about the structure, instructions and types of questions that may come up. You can find out how many questions you have to answer, how many sections each paper is divided into, how many marks each answer is worth, if any questions are compulsory. They even help you to anticipate the type of question that might be asked.
Past papers also enable you to practise dividing up the time given to complete all the parts of the exam and to judge how well-prepared you are. It is a good idea to practise doing a past paper under timed conditions on a regular basis. This will allow you to check the rate at which you can answer the questions and give you an idea of what you can achieve within the set time.
JG.
SET SMART GOALS FOR IELTS
Setting goals is a significant step for planning ahead and staying on top of your studies. If you have specific goals and reasons for achieving them, you are more likely to be successful. You can begin by brainstorming some ideas relating to your goals. Next, get more specific and adapt them to fit into a SMART #IELTS model.
SMART is an acronym and stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time based. You should aim to fulfil the SMART criteria for each of your goals.
SPECIFIC.
Be specific rather than general. To narrow down the goal, ask “Wh…?” questions, such as what? where? which? and why? For example, you might want to see what your particular strengths and weaknesses are in Reading, Writing, Listening and Speaking.
MEASURABLE.
A goal needs to be measurable so that you can monitor your progress. For example, what #IELTS band score are you hoping to achieve.
ACHIEVABLE.
Take a reality check and set goals that are achievable. Be ambitious, but make sure that your goals are realistic. For example, you cannot aim to achieve an #IELTS band 9 score when you are a lower-level language student in one month.
RELEVANT.
Is the goal relevant to your progress? For example, is it a target that is based on your particular needs and not one that someone else has set for themselves.
TIME BASED.
How much time do you need to achieve the goal? Set a time limit.